When you register a domain, one of the first things you’ll be asked is whether you want to protect your privacy. Domain protection and privacy go hand in hand, but they’re not the same thing. Your domain can be private, but it can also be unprotected if you don’t take steps to secure it. 🔒
Domain protection is a broad term that encompasses a lot of practices you can put into action to ensure your domain doesn’t fall into the wrong hands. Protecting your domain and securing its privacy means you’ll be able to avoid getting spam, phishing, and stealing attempts.
👉 In this article, we’ll talk about what it means to protect your domain, how that’s different from making it private, and how it works. Let’s get to it!
What is domain protection?
Domain protection is a catch-all term for tools and actions you can use to protect against unauthorized actions. For example, if someone tries to log into the domain registrar where you purchased a domain and transfer it, some type of protection functionality should kick in.
What that functionality looks like will depend on the registrar you use. Some services will ask for Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) or institute cooldown periods before the transfer goes through. This way, the real owner of the domain will be able to stop the unauthorized transfer in time.
There are a lot of domain protection features you can look for in a web host. At their core, these features should protect you against unauthorized transfers, Domain Name System (DNS) updates, and even registry expiration.
Later in this post, 👇 we’ll discuss some specific domain protection features that you’ll want to look for and implement to keep your domains secure.
The differences between domain protection and domain privacy
Next, let’s cover domain protection vs domain privacy because, while there is some overlap, these two terms refer to different things.
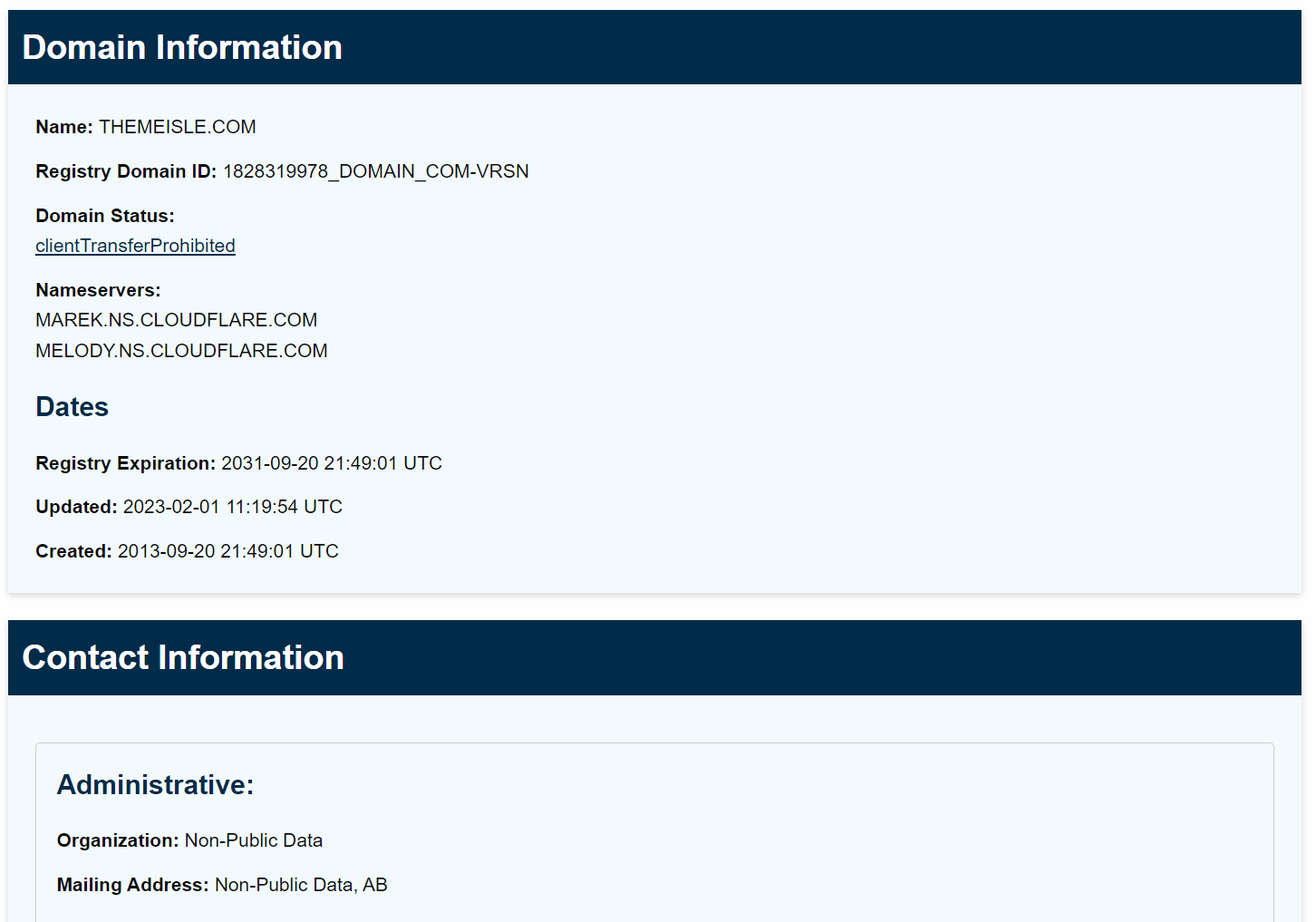
When you register a domain, all the information goes into a database called WHOIS. It includes a lot of personal data for each registrant, including name, address, and contact information. For a lot of people, that’s information they’d rather not make public on the web.
We say public because anyone can look up a domain in the WHOIS database using a multitude of services. A simple search can reveal who registered a domain and all the information associated with it.

If you’ve ever registered a domain without making your information private, you’ll be familiar with spam messages, fraudulent buying offers, and various degrees of harassment. That’s what makes domain privacy such a popular option.
Domain privacy, or WHOIS “protection,” means your registrar keeps your information safe by entering a third party’s data in the database. Instead of your name appearing, the domain will show up as registered to a business, with the registrar acting as the intermediary.
From a practical standpoint, nothing changes for you except that your information will be safe.
Domain protection, on the other hand, involves security measures that your web host or registrar can take to protect your actual domain name, not just your personal information.
That means the registrar puts security measures in place to prevent other people from gaining access to the domain and making changes to it. You can implement domain protection measures on a property that uses (or doesn’t use) WHOIS privacy, as they’re different types of services.
How domain protection works (2 components)
What domain protection measures you get access to will depend on your web host or registrar. The options we’re going to cover below are the most important in terms of security. If you’re about to register a new domain, these are the options you should be on the lookout for.
1. Domain privacy
Although domain security and privacy aren’t the same, they go hand in hand. If your registrar offers an option to keep your information private while setting up a new domain, we recommend you take it.
If attackers don’t know who registered a domain, getting access to it will be a lot more difficult. They won’t be able to send any phishing attempts or try to brute force their way in using information, such as your email address.
There’s no reason to opt out of domain privacy nowadays. A lot of reputable domain registrars have moved on to offer it for free, which makes it a no-brainer.
If your registrar charges you a fee for domain privacy, consider using a different option. Even if the fee isn’t high, it’s still an extra cost you’ll need to pay yearly, and it’s one that you can avoid.
2. Authenticating changes to the domain
Making changes to a domain can mean anything from transferring it to a new owner to changing nameservers, turning off auto-renew, or changing contact info. In practice, most people don’t make changes to their domains often, so your registrar should always verify your identity if you do.
Identity verification can come in many forms. Your registrar or web host might use 2FA or attempt to reach you via email or phone. They might even ask you to submit documentation, depending on the registrar and your security settings.
What authentication methods you can choose from will depend on the registrar and the options they offer. Our recommendation is to always use the highest level of security possible to avoid anyone trying to steal the domain.
Verifying your identity may be a hassle, but it’s something you’ll almost never need to do. It also helps eliminate the risk of losing the domain (unless you choose not to renew it), which makes it worth the effort.
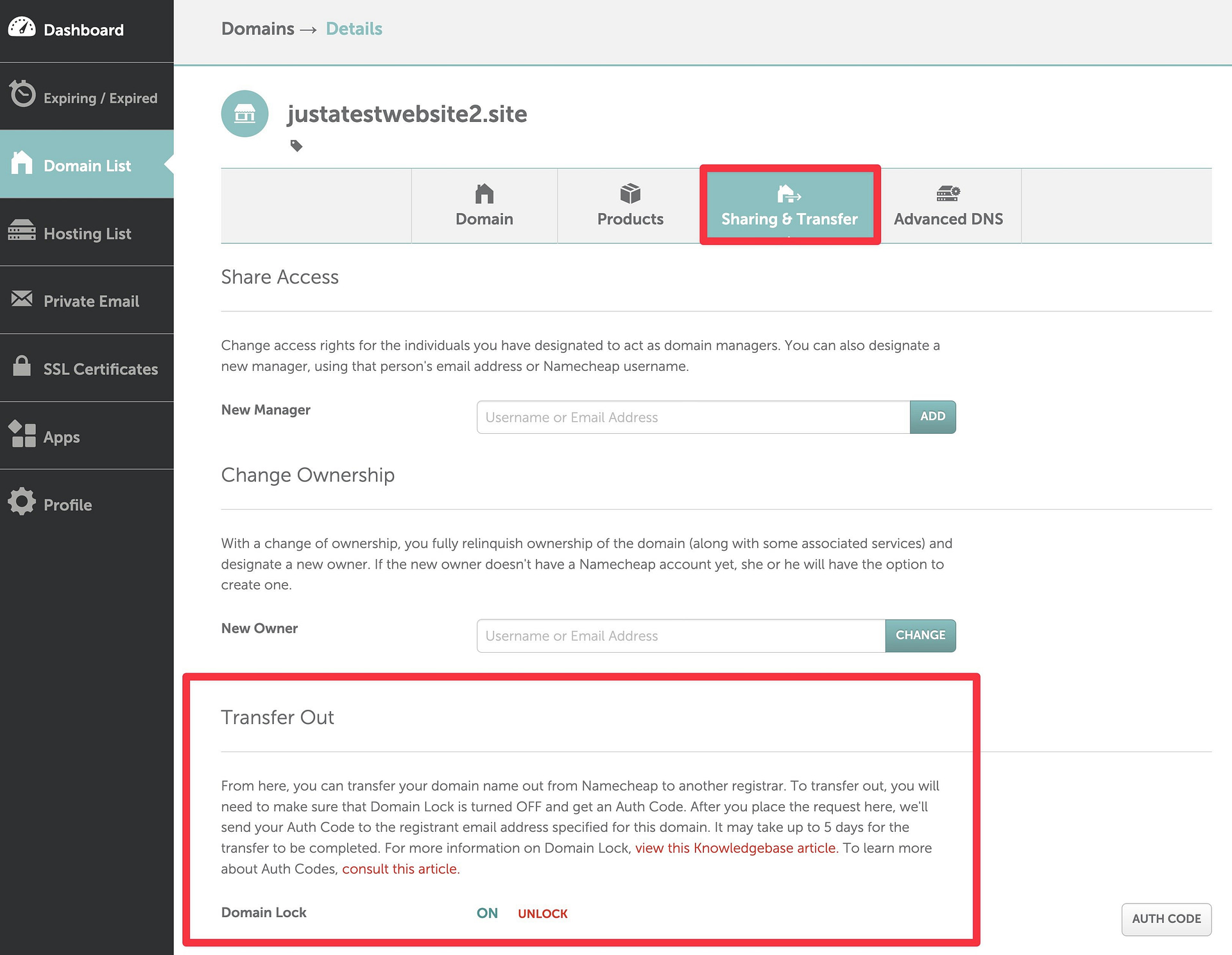
Beyond setting up two-factor authentication, you’ll also want to ensure you’ve enabled Registrar Lock at your domain registrar. When enabled, this adds extra protection to prevent your domain from being transferred to a different registrar. You should only disable this setting if you’re in the process of moving your domain name to a new registrar.
Most quality registrars will enable Registrar Lock by default. However, you might still want to double-check that you didn’t accidentally disable it. You’ll usually find these settings somewhere in your domain management panel – consult your registrar’s documentation if you need any help.
👉 Here’s what it looks like at Namecheap:
Set up domain protection today 🚀
Domain protection and privacy are essential for every address you register. Combining these solutions together means you’ll be able to avoid spam related to the domain as well as attempts to steal it.
Considering how important a domain can be to your website and brand identity, you want to take every measure possible to avoid losing it.
In terms of protection, you should be on the lookout for registrars that offer domain privacy and authentication. The latter will kick in when you or someone else tries to make changes to a domain, and they’ll need to verify their identity before they get through. 🔒
Do you have any questions about how domain protection works? Let’s talk about them in the comments section below!















Or start the conversation in our Facebook group for WordPress professionals. Find answers, share tips, and get help from other WordPress experts. Join now (it’s free)!